By NexGen Support Team
January 13, 2025

Tax season can feel overwhelming, especially when you’re faced with different IRS tax forms like Form 1040, Form 1099, and W-2 that are used for tax purposes. Whether you’re a freelancer, self-employed, or just trying to get a better handle on your taxes, understanding 1040 vs 1099 is key. Each form has its role in reporting income to the IRS. It’s important to understand what they do and which ones to use for filing taxes. In this blog, we’ll walk you through the basics of each form, who needs to file them, the due dates for filing, and how they affect your taxes. Don’t worry—we’ll make it simple, so you can confidently approach the tax season.
1040 is the main form in the United States. It shows your income, including wages and tips. It gives an earnings summary of your financial year for taxes.
This form helps you reduce your tax bill. You can do this by claiming deductions, tax credits, and exemptions. One option is the standard deduction, which lowers your income. You can also choose itemized deductions. These may include medical costs or taxes, which can lower your taxable income.
If you earn more than a certain amount in the U.S., you usually have to file a federal tax return. You will use Form 1040 for this.
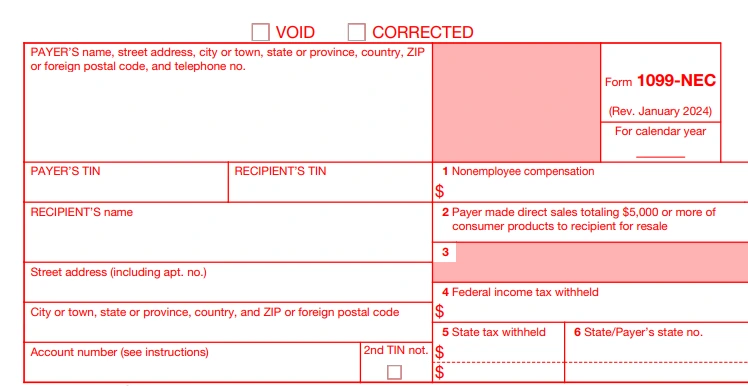
Use the form 1099 to report various types of income, including non-employee compensation, for the tax year
It is different from a W-2 form, which is for employees. A 1099 Form is used to show income for non-employees, like contractors or freelancers. It covers several types of income, including rent, royalties, and prizes.
Receiving a 1099 means you made money and no taxes were taken out. You need to tell the IRS about this money and pay taxes on it. This is very important for people working in the gig economy and for small businesses.
Is a Form 1040 the same as a 1099? No. They are both IRS Forms, but they are used for different things. Here is a simple table that shows the main differences:
| Feature | What is a 1040? | What is a 1099? |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | To file a person’s annual income tax return. | To report specific types of earnings to the IRS and the person receiving it. |
| Who files it? | Individuals file this form with the IRS. | Businesses or payers file this form with both the IRS and the recipient. |
| Types of income reported | Reports all income the taxpayer receives, such as wages, salaries, investments, and self-employment income. | Reports income like payments to independent contractors, interest, dividends, rents, and royalties. |
| Deadlines for filing | By April 15th of the year after. For example, report your 2023 income by April 15th, 2024. | Send it to recipients and file it with the IRS by January 31st. If January 31st falls on a weekend or a holiday, the deadline will move to the next business day. |
Knowing these differences is key for reporting income correctly and following IRS rules.
Before you start, get all the documents you need. This will make things easier, reduce mistakes, and help everything go smoothly. Also, keep your financial records organized to prepare your taxes and keep accurate records.
How to complete Form 1040? You will need certain important documents. Getting them ready can help you file more quickly:
Before sending your return, make sure you have all the necessary forms. They include:
To learn more about Form 1099 and tax filing for freelancers or independent contractors and changing your status from freelancer to W-2 employee, read our detailed blog.

File your income tax return using form 1040 and pay your taxes by due date
Filing your income tax return may feel hard due to many documents and rules. To make it simpler, just follow these easy steps. This will help you and ensure your return process goes smoothly.
Your filing status is very important for taxes. It influences what you need to provide, the credits you can get, the deductions, and how much tax you owe. Picking the right status can help you get benefits. The IRS gives several options: Single, Married Jointly, Married Separately, Head of Household, and Qualifying Widow(er) with a Dependent Child.
Your status relies on your marriage situation and whether you have dependents. To file correctly, select the best status for your case.
Report Your Income:
Claim Your Deductions and Exemptions:
The Adjusted Gross Income (AGI) is calculated as your total income minus the eligible deductions and exemptions you claim.
Calculate it by applying the applicable rate on AGI. Adjust deductions like child tax credit and any taxes withheld information to further reduce your tax payable.
Finally, report your liability. You would see the amount you owe and make the payment, or the refund you can expect in your account or mode of receipt of your choice.
Filling out tax forms for the first time can feel hard, but these tips can help you do it correctly:
Understanding the 1040 vs 1099 forms is key for filing your taxes. Each has its purpose. This means you should know when and how to use them. At NexGen Taxes, we are here to help you with all your tax filing needs. We will make it easier for you. Stay informed and organized to get the best out of your tax filing experience.
Filing 1099 is easy through NexGen Taxes. Our platform helps you handle tax filing smoothly. It is simple to use and has all the features you need. Whether you are filing a 1099 or a 1040, NexGen gives you the support you need.
Streamline your tax process with the NexGen Taxes team! Our expert tax professionals are ready to simplify the complexities, maximize your deductions, and boost your savings. Start today and confidently take control of your tax journey!
The penalties for filing late depend on the tax you owe and the delay period. Usually, if you don’t file on time or pay on time, you may face penalties. Additionally, if you don’t pay enough, interest can build up on the amount you owe. If you keep delaying your payments, the penalties can increase over time.
Yes, you can file your taxes online using your 1040 and 1099. Many online tax filing services allow you to import your 1099 information into your 1040 tax form.
Ask a trusted tax advisor for help if you have questions about which forms to use or other tax-related topics. You can also contact the IRS through their official website or phone number to get the IRS form 1040 instructions and IRS form 1099 instructions. It is a good idea to seek tax expert advice if you feel unsure about your tax responsibilities.
The main difference lies in their purpose and who they are intended for. The 1040 form is used by individuals to report their annual income and calculate how much tax they owe or are owed by the IRS. On the other hand, the 1099 is used by businesses to report payments made to independent contractors or freelancers. Lastly, the W-2 form is issued by employers to employees to report their wages and taxes withheld throughout the year for tax filing purposes.
Yes. If you receive a 1099, you need to report that earning on your 1040 tax return. This ensures that all your earnings are counted and taxed correctly.
Self-employed people often use Form 1040 to show their earnings and expenses. But employees also use this form. Both self-employed people and employees need it for their income tax requirements.
Yes, they are required to fill out a 1040 when filing their taxes. The 1099 form reflects their other earnings as independent contractors, which must also be reported on their 1040 tax return for accurate taxation.
Independent contractors or freelancers who receive a 1099 instead of a W-2 must complete a 1040 form. This form is used to file their income tax return each year.
In the U.S., if you earn more than a specific amount, you need to fill out a 1040. Companies or payers hand out a 1099 form. This is used to report earnings to the IRS and the individuals who receive that income.
Yes, individuals can file both a 1040 and report income from a 1099 form in the same tax year. The 1040 form encompasses all sources of income, including those reported on a 1099. It is essential to accurately report all income sources to ensure compliance with tax regulations.
If you don’t report all your earnings, you could face penalties from the IRS. Accurate reporting all income sources is crucial to avoid any legal issues. Properly reporting your earnings ensures compliance with regulations and avoids potential consequences.
Yes, self-employed individuals who receive income on 1099 forms can deduct business expenses related to that earning. Keeping detailed records of expenses is crucial for accurately reporting deductions and reducing tax liability.
Tax rates differ for 1099 income depending on earnings and filing status. Independent contractors pay income and self-employment taxes. Consulting a tax professional is crucial to grasp your tax responsibilities and deductions.
Yes, 1099 income is typically considered self-employment income. Independent contractors and freelancers often receive income on a 1099 form, indicating that they are responsible for paying self-employment taxes on that earnings.
© 2022-2026 NexGen Unlimited, LLC